special tests for foot drop|differential diagnosis for foot drop : department Store The common peroneal nerve is the smaller and terminal branch of the sciatic nerve which is composed of the posterior divisions of L4, 5, S1, . See more Resultado da We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBGás 24 horas em Rio das Ostras. Compre Gás de Cozinha Online com menor Preço do Gás aqui. Tel: 0800-000-0960 Gás 24 horas. Aplicativo da Preço do Gás. Entrega de Gás Rápida em Rio das Ostras. Preço do Gás; Rastrear Pedido; Revendedor; Notícias; Cadastre-se; Gás; Contatos; Pedir gás agora; Gás 24 horas em Rio das Ostras
Foot drop also known as drop foot is not a disease, but rather a commonly encountered symptom of a neurological, anatomical, or muscular problem. Foot drop is inability to lift the forefoot due to the weakness of dorsiflexors of the foot. Ankle and foot dorsiflexors, namely the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum . See moreThe common peroneal nerve is the smaller and terminal branch of the sciatic nerve which is composed of the posterior divisions of L4, 5, S1, . See moreLesion site localization of foot drop can be challenging because it may be a presentation of a range of pathologic conditions that localize along the full course of upper and lower motor neuron pathways which often overlap in clinical presentation.The . See moreTypical presentation of foot drop can be noted when testing the foot and ankle in isolation, however, in a clinical setting, it may be identified . See more
Foot drop is usually diagnosed during a physical exam. Your health care provider will watch you walk and check your leg muscles for weakness. Your provider also may check . Foot drop (sometimes referred to as "drop foot") refers to an inability to lift the forefoot due to weakness of the dorsiflexors. This condition may be the result of a muscular, .
In cases where unilateral foot drop occurs spontaneously in a previously healthy patient, further investigation into metabolic causes (eg, diabetes, alcohol abuse, and exposure to toxins) is. Foot drop is an inability to lift the forefoot due to the weakness of the dorsiflexors. This may result from muscular, skeletal, or nervous system pathology. A thorough evaluation .

Foot drop can be diagnosed by several types of physicians. If the lower back is suspected as a cause, it may be advisable to see a spine specialist, such as a physiatrist, orthopedic surgeon, or neurosurgeon. Diabetes or other .The provider may order any of the following tests to find the underlying cause of foot drop: Imaging tests, such as X-rays , ultrasound and/or MRI scans, to look for compression or . Foot drop isn't a disease. Rather, it is a sign of an underlying neurological, muscular or anatomical problem. Sometimes foot drop is temporary, but it can be permanent. .
Foot drop is when you have difficulty lifting the front part of your foot. This may cause you to drag your foot when you walk. Foot drop, also called drop foot, can be caused .Nerve tests. These tests show how well and how fast the nerves send electrical signals to your muscles. Imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan. These tests can show pressure on a .The painful conditions of the ankle and foot are very common presentations and most commonly caused by trauma or injury related to sport activities. It is important to be familiar with some basic physical exam maneuvers necessary .
Quiz yourself with questions and answers for Special Tests: Foot/Toes, so you can be ready for test day. Explore quizzes and practice tests created by teachers and students or create one from your course material. . navicular drop test. midtarsal/intertarsal joint glides. 3 of 26. Term. intermetatarsal neuroma. pencil test, mulder's sign .Foot/Ankle Joint. Shoulder Joint. Elbow Joint. Wrist/Hand Joints. Our philosophy: Special tests are meant to help guide your physical examination, not be the main source of your information. There are hundreds upon thousands of Special .
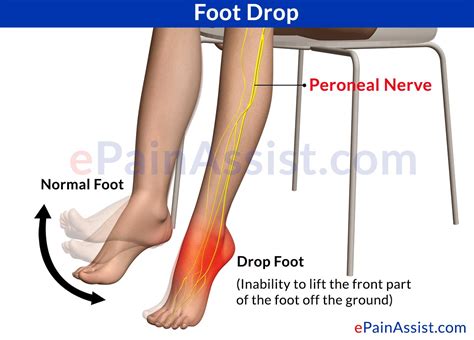
A patient recovering from surgery to treat foot drop, with limited plantar and dorsiflexion.. Foot drop is a gait abnormality in which the dropping of the forefoot happens out of weakness, irritation or damage to the deep fibular nerve (deep peroneal), including the sciatic nerve, or paralysis of the muscles in the anterior portion of the lower leg.It is usually a symptom of a greater problem .
Special Tests are orthopedic diagnostic tests that help identify the nature of musculoskeletal conditions. These special tests are used in creating a proper treatment plan or therapy for a patient’s injury or condition. Special Tests: Physical Examination Special tests. straight leg raise. compression of lower lumbar nerve roots (L4-S1) important to distinguish from hamstring tightness. . Foot drop. Common peroneal nerve palsy or sciatic nerve compression. Lateral knee compression. Hip dislocation. Quadriceps weakness. Femoral nerve palsy.Foot - Special Tests (5 P) H. Hand - Special Tests (13 P) Hip - Special Tests (15 P) K. . Pages in category "Special Tests" The following 200 pages are in this category, out of 222 total. (previous page) . Drop Arm Test; E. Effusion tests of the Knee; Ege's Test; Elbow extension sign; Elbow Flexion Test;
unusual reasons for foot drop
The Navicular Drop Test is a test to assess for pes planus and overpronation which can be a factor in plantar fasciitis/heel pain . Now ask your patient to bear weight on the foot and measure the distance from the ground to the tuberosity again and mark it on the same paper. . Statistical Values for all Special Tests from the latest .
Apley test – Pain at the medial or lateral joint McMurrays test – Pain or a reproducible click; Special Test: McMurray’s Test PURPOSE: Testing for Injury to the Menisci ; Video Demo Instructions, Procedure, Positive Test: Special Test: .Heel Thump Test: PROCEDURE: the patient is in seated or supine; the examiner uses one hand to stabilize the leg; with the other hand, the examiner applies a firm thump on the heel with the fist so that the force is applied to the center of the heel and in line with the long axis of the tibia.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Height of steps: high-stepping gait is associated with foot drop, which can be caused by peroneal nerve palsy (e.g. trauma, surgery). Ask the patient to walk on their tip-toes and then on their heels to further screen for pathology. Patient’s with arthritis or lower limb muscle weakness will struggle to perform these tasks. . Special tests .
The provider may order any of the following tests to find the underlying cause of foot drop: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound and/or MRI scans, to look for compression or damage in your legs, spine or brain. Certain blood tests, such as a blood sugar test to check for diabetes and diabetes-related neuropathy. Foot drop, characterized by the inability to lift the forefoot due to weakness in the dorsiflexion of the foot, poses diagnostic and management challenges seldom encountered in primary care settings. This continuing medical education (CME) activity aims to equip healthcare professionals with a comprehensive understanding of foot drop, exploring .SLR Test/ Straight Leg Raise Test: PURPOSE: to determine the cause of low back pain. VIDEO DEMO, PROCEDURE, POSITIVE SIGNS: Herniated Disc - If the patient experiences sciatic pain when the straight leg is at an angle of between 30 and 70 degrees.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Trendelenburg's Sign/ Trendelenburg's Test: Testing for: the strength of the Gluteus Medius Muscle. VIDEO DEMO, PROCEDURE, Technique, POSITIVE SIGN: Gluteus medius is weak if the pelvis on the affected side pops out or drops3. Special Test: Tibial Torsion Test PROCEDURE (Prone): knee flexed to 90°. the examiner views from above the angle formed by the foot and thigh after the subtalar joint has been placed in the neutral position, noting the angle the foot makes with the tibia.
The navicular drop test is a method used to assess the degree to which the talus plantar flexes in space on a calcaneus that has been stabilized by the ground, during subtalar joint pronation. This test was introduced firstly by Brody in 1982 to assess the amount of foot pronation in runners. See Also: Foot Anatomy
Hip / Pelvis Special Tests: Click on the Name of the Special Test to go to its Page (includes Purpose, Procedure /Video Instructions, Positive Sign): Ely’s Test Patrick’s Test FABER Test Gaenslen’s Test Ober’s Test Straight Leg Raise Test Lasègue Test Thomas Test Trendelenburg’s SignSpecial Test: Mortons Neuroma aka Metatarsal Squeeze Test: Video Instruction, Procedure, Purpose, Positive Test:Patient is seated Compress the foot by applying pressure to the medial and lateral aspects of the foot at the metatarsophalangel joints
unable to dorsiflex foot
Special Test: Leg to Heel Alignment: POSITIVE SIGN: If the lines are parallel or in slight varus (2° to 8°), the leg-to-heel alignment is considered normal. If the heel is inverted, the patient has hindfoot varus;
Description [edit | edit source]. This windlass mechanism is a mechanical model that describes the manner in which plantar fascia supports the foot during weight-bearing activities and provides information regarding the biomechanical stresses placed on plantar fascia.. The windlass test achieves a direct stretch on the plantar aponeurosis which can be effective in examining . Special Tests are orthopedic diagnostic tests that help identify the nature of musculoskeletal conditions. These special tests are used in creating a proper treatment plan or therapy for a patient’s injury or condition. Special Tests: Physical ExaminationTest to determine if there is excessive pronation of the foot-patient is standing, measure the distance between the navicular tuberosity and floor with foot in both natural stance and subtalar neutral. (positive for drop if there is greater then 10mm difference between the measurements)
examiner uses their other hand to graps the dorsal surface of the foot, combining eversion and plantarflexion of the foot and applying overpressure. Assess Middle Fibers of the Deltoid Ligament: examiner repositions their hand so the calcaneus is grasped ( still stabilizing the anterior surface of the tibia and fibula proximal to the ankle with .The Navicular Drop Test (NDT) was first described by Brody in 1982 as a means of quantifying the amount of foot pronation in runners. It is the one of the static foot assessment tool and is intended to represent the sagittal plane displacement of the navicular tuberosity from a neutral position i.e. Subtalar joint neutral to a relaxed position .
4 de jan. de 2023 · How to give feedback, with examples. Giving constructive feedback can be tougher than you may assume and take some skills and practice to master. .
special tests for foot drop|differential diagnosis for foot drop